relative risk in spss|Relative Risk: Definition, Formula & Interpretation : Baguio Making sense of odds ratios and relative risk estimates in SPSS Statistics - Smart Vision Europe. Estimating the degree to which the risk of an event or outcome is increased or decreased based on a condition is a . Tanker Services Marlow. Our professional tankering fleet are available for liquid waste removal and tank emptying. We have a fleet of suction tankers and jet vacs that can safely and effectively carry out: Non-hazardous liquid waste removal (Food waste, Production by-products, Flood relief) Hazardous liquid waste removal Sewage waste removalAnalyze the Domain Authority (DA) of a website with the free Moz DA & PA checker. Gain insight into site performance, keyword, and competitor research for your site or a competitor with a single click.
relative risk in spss,SPSS can be used to determine odds ratio and relative risk values for various types of data. This video demonstrates how to calculate odds ratio and relative risk values . V4.17 - Relative Risk Analysis in SPSS - YouTube. 0:00 / 3:14. V4.17 - Relative Risk Analysis in SPSS. how2statsbook. 5K subscribers. Subscribed. 86. 23K views 4 years ago. From.Relative Risk: Definition, Formula & Interpretation 8.9K views 3 years ago. How to compute Odd ratio and relative risk in SPSS.This tutorial video show what's Odd Ratio and its calculation as well as how to use it in the interpretation risk.The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful. However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative .
Making sense of odds ratios and relative risk estimates in SPSS Statistics - Smart Vision Europe. Estimating the degree to which the risk of an event or outcome is increased or decreased based on a condition is a .What is Relative Risk? Relative risk is the ratio of the probability of an adverse outcome in an exposure group divided by its likelihood in an unexposed group. This statistic indicates whether exposure .Multinomial Logistic Regression | SPSS Data Analysis Examples. Version info: Code for this page was tested in SPSS 20. Multinomial logistic regression is used to model nominal outcome variables, in which the log .
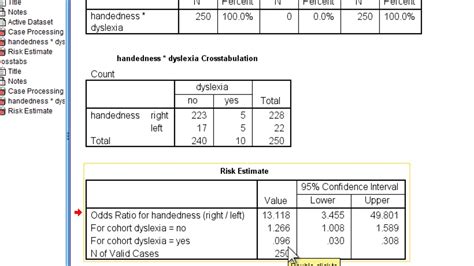
The estimation of relative risks (RR) or prevalence ratios (PR) has represented a statistical challenge in multivariate analysis and, furthermore, some . The Risk Estimate table shows the odds ratio, the two risk ratios, and confidence intervals for each. The first risk ratio is 1.53, which is computed by dividing 70% by 45.7%. This risk ratio can be interpreted .
I am interested in conducting binary logistic regression analyses for a cohort study on SPSS, but I would like to use relative risk (RR) to express my results rather than odds ratio (OR).

Standard reporting practice is to report the odds ratio in terms of the incidence of the adverse event (death), and both the odds and risk ratios relative to the control condition; i.e., having the control condition appear in each ratio's denominator. To conform to this standard, code the variables so that the Experimental, Died count is in the . In fact if you know the Odds ratio for one cell, you can find the odds ratio for all cells. Odds ratio for female/male who died = 0.088. This is also the odd.
Odds ratios (OR) significantly overestimate associations between risk factors and common outcomes. The estimation of relative risks (RR) or prevalence ratios (PR) has represented a statistical challenge in multivariate analysis and, furthermore, some researchers do not have access to the available methods. Objective: To propose and .SPSS includes relative risk ratios in the output, under the column “Exp(B)”. The relative risk ratio for a one-unit increase in the variable write is .9437 (exp(-.0579284) from the output of the nomreg command above) for being in .
Using SPSS to calculate the Relative Risk (Risk Ratio). From Chapter 4 of my *free* textbook: How2statsbook.Download the chapters here: www.how2statsbook.comMore chapters to come. Subscribe to be . Untuk menghitung relative risk menggunakan SPSS, Anda dapat mengikuti langkah-langkah berikut: Buka data set Anda di SPSS dan pastikan data sudah terstruktur dengan baik, misalnya kolom untuk variabel terpapar dan tidak terpapar, serta kolom untuk variabel hasil. Pilih menu Analyze > Descriptive Statistics > Crosstabs.
Relative risk of disease, exposed vs. not exposed: RR = a/(a+b) / c/(c+d) = a(c+d) / c(a+b) = 0.0141/0.0239 = 0.592. Odds. Oddsis the likelihood of an event divided by the likelihood of a non-event . Odds of the disease in each group: . Easierway: use logistic regression in SPSS, even if you have only one independent variable with two levels .In statistics, risk is a probability, usually relating to an adverse event (i.e., something bad). To calculate relative risk (RR), you must know all subjects’ exposure statuses and outcomes. Before learning how to calculate it, you first need to know about absolute risk. Absolute risk (AR) is simply the number of events divided by the number .Example Data: Odds ratio versus relative risk. A hypothetical data set was created to illustrate two methods of estimating relative risks using Stata. The outcome generated is called lenses, to indicate if the hypothetical study participants require corrective lenses by the time they are 30 years old.relative risk in spss In this scenario, we would calculate the relative risk as: Relative Risk = P (event in treatment group) / P (event in control group) Relative Risk = P (disease with exercise) / P (disease with no exercise) Relative Risk = 0.28 / 0.50. Relative Risk = 0.56. Since the relative risk is less than 1, this tells us that this disease is less likely to .
relative risk in spss Relative Risk: Definition, Formula & InterpretationYes, If you perform survival analyses using the KM test with the SPSS you will obtain the curves but the results are not adjusted for confounding factors. With Cox regression you can adjust for .

The relative excess risk due to interaction (RERI) provides a useful metric of departure from additivity of effects on a relative risk scale. In this paper, the authors show that RERI is identical to the product term in a linear odds ratio or a linear relative risk model. SAS and STATA codes are provided for fitting a linear odds ratio model .
Parameter Estimates. n. B – These are the estimated multinomial logistic regression coefficients for the models. An important feature of the multinomial logit model is that it estimates k-1 models, where k is the number of levels of the outcome variable. In this instance, SPSS is treating the vanilla as the referent group and therefore estimated a .
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright .
Odds ratio versus relative risk. Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret. The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful. However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be used . The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group. It is calculated as: Relative risk = [A/(A+B)] / [C/(C+D)] In short, here’s the difference: An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds. Relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities.
relative risk in spss|Relative Risk: Definition, Formula & Interpretation
PH0 · V4.17
PH1 · SPSS Video #10
PH2 · Relative Risk: Definition, Formula & Interpretation
PH3 · Problem 7.2: Risk Ratios and Odds Ratios with SPSS
PH4 · Odds Ratio versus Relative Risk
PH5 · Multinomial Logistic Regression
PH6 · Making sense of odds ratios and relative risk
PH7 · How to cumpute Odd ratio and relative risk in SPSS
PH8 · How to Interpret Relative Risk (With Examples)
PH9 · A simple method for estimating relative risk using logistic